Internal Medicine
The Internal Medicine Residency Training Program in Sultanate of Oman is organized under the auspices of Oman Medical Specialty Board (OMSB). It requires the successful completion of four years of full-time training in accredited centers and regular evaluations and formal examinations to ensure that candidates will obtain the knowledge, skills, attitude and experience required for the provision of high quality care in Internal Medicine.
The Internal Medicine Education Committee will strive to ensure that all Internal Medicine trainees possess sound knowledge, skills, attitude and experience through uniform high quality training.
To produce well-trained and competent Internist capable of providing excellent healthcare.
By the end of their training, the residents should be able to:
Apply the principles and practice of Internal Medicine.
Be proficient in taking history and performing complete physical examination.
Be skilled in summarizing a case and formulate a sound working diagnosis.
Select appropriate diagnostic tests for a given patient.
Formulate sound management plans based on evidence-based practice.
Provide continuous care to the patients and their families on a long-term basis when required.
Identify and manage common emergencies and life- threatening conditions.
Communicate effectively with colleagues, other health care team members and allied healthcare both in hospital and in the community.
Communicate with patients and their families on different health care issues.
Keep comprehensive and appropriate written communications.
Manage referrals from other health care facilities.
Teach and supervise junior colleagues and other health care staff.
Demonstrate lifelong learning skills.
Demonstrate skills to conduct medical research.
Maintain high standards of professionalism and medical ethics.
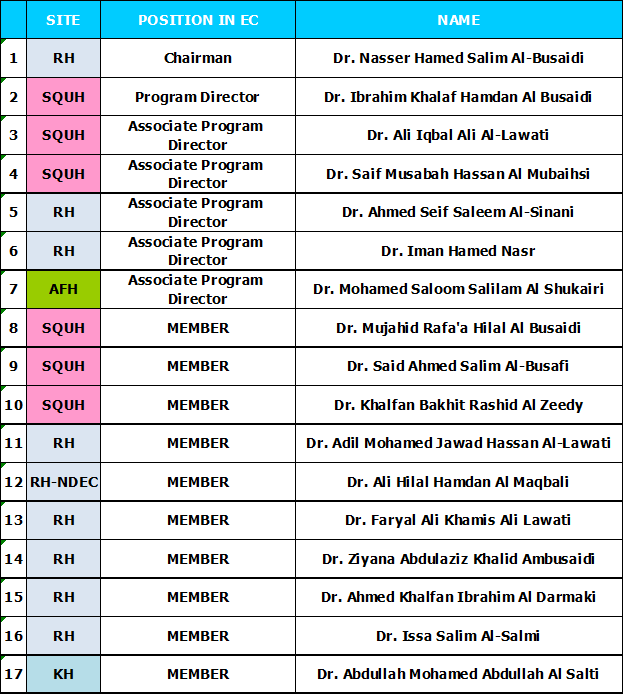
INTERNAL MEDICINE EDUCATION COMMITTEE MEMBERS
ROTATION OUTLINE
The program extends over a period of four years. Residents may extend their training for up to one year after the approval of the Education Committee. The training periods are divided into 13 blocks, each block is comprised of 4 weeks or 28 days.
First Year
ACLS: Resident must have ACLS before joining to OMSB or within the first 6 months.
Note:Residents are required to take End-of-Year Exam at the end of the first year of training for promotion to the next level.
Second Year
Note: Residents are required to take End-of-Year Exam at the end of the second year of training for promotion to the next level. They are also required to take OMSB Part I examination.
Third Year
Note: Residents are required to take End of Year Exam at the end of the third year of training for promotion to the next level.
Fourth Year
Note: By the end of the fourth year, a final assessment of the resident will be done by the Program Director and decide whether candidate fulfilled the requirements to do the OMSB (Internal Medicine) part 2.
OUTLINE OF MAJOR AND MINOR ROTATIONS
MAJOR AND MINOR ROTATIONS
Training Centers
1. Sultan Qaboos University Hospital
2. Royal Hospital
3. Armed Forces Hospital
4. Khoula Hospital
Regional Hospital for other Rotations and/or Electives
1. Al Nahdha Hospital – Dermatology Elective
2. Al Massarah Hospital - Psychiatry Elective
Minimum Requirements for Admission:
The applicant must obtain a bachelor degree in medicine and surgery or equivalent from an accredited college or university.
The applicant must complete the internship year successfully.
The applicant should be medically fit.
The applicant must pass the entrance examinations and interviews as well as complete the registration requirements.
Program Specific Criteria:
1. Final MD grade in Medicine
2. Evaluation in Medicine rotation during internship.
3. To interview applicants with 1st and 2nd choices of Medicine, (i.e. fill vacancies with 1st choices and complete with 2 choices)
4. Applicants should ask the recommendation letters to be forwarded directly to OMSB.
5. A self-declaration that the applicant is mentally and physically fit to do on-call duties.
6. Additional basis of grade us applicant's active participation in Research, conferences and/or other scholarly activities.
ASSESSMENT AND FEEDBACK
Introduction
Assessment plays a central role in medical education at all levels of training. There are two general reasons for this assessment. First, from a quality assurance perspective, assessment is seen as the primary mechanism by which both institutions (e.g. hospitals) and organizations (professional licensing and certifying bodies such as OMSB) can assure the public of acceptable levels of competence among their trainees and practitioners. Second, from an educational perspective, assessment is seen as a primary mechanism for providing feedback to trainees and practitioners for the purposes of improving performance.
There are OMSB forms that are used in evaluation of the resident by the supervisor and the team, with one of the form being used for evaluation by the resident towards the team. These forms are available in the New Innovations System.
GENERAL OMSB EVALUATION TOOLS:
1. In-Training Assessment Report (ITAR)
2. Evaluation for Procedural Skills
3. Evaluation for Presentation
4. Evaluation for Journal Club Presentation
5. Evaluation for Mini-Clinical Exercise (Mini-Cex)
6. Evaluation for Case-Based Discussion
7. Multi Source Feedback (360 Degrees Evaluation)
8. Rotation Evaluation by Residents
9. Trainer Evaluation by Residents
10. Trainer/Education Committee Member Evaluation
11. Research Block Evaluation
12. Research Mentor Evaluation
13. Six-Monthly and Annual Evaluation
14. Final In-Training Assessment Report (FITAR)
15. Program Evaluation by Residents
16. Program Evaluation by Faculty
PROGRAM SPECIFIC EVALUATION FORM:
1. Educational Supervisor’s Comments/ Feedback Evaluation
2. Mini-Form Evaluation for Clinic Rotation
3. Mini-Form Evaluation for Research Block Rotation
4. Pre-Research Elective Approval Checklist
5. Research Mentor and Co-Mentor Agreement Form
EXAMINATION OUTLINE:1) End of Year Exam (Progression exam) Given for R1, R2 and R3 levels THE FORMAT OF THE EXAM:
A written examination of MCQ (Multiple Choice Question) type of single best answers. The passing mark for the exam is decided each year based on standard settings decided by the Exam Department. The exam will be taken in June / July of each academic year, but those candidates who fail the 1 st attempts will be given a chance for a Re-sit exam which is usually one month after the exam. A resident who fails both, End-of-Year and Re-sit Exam will have to repeat the year at the same residency training level.
For Senior Residents (R3). Each resident will undergo a supervised clinical exam organized by the program's examination subcommittee. The exam is divided into 8 stations with real patients and surrogate patients. (4 Clinical stations, 1 History taking Skills, 1 Communication Skills, 1 Emergency Scenario and 1 Office Scenario). The exam is usually conducted in July; dates are decided by the Exam Subcommittee. 2) OMSB PART 1 EXAMINATION The examination is a qualifying examination. A resident must pass OMSB Part-I Examination before attempting the Final Examination to obtain the Specialty Certificate. A Resident is allowed three (3) attempts to pass the OMSB Part I Exam. This exam can be attempted at R2; however, the Education Committee may selectively allow a resident who is competent to do OMSB Part I Exam at the end of R1. No R3 Residents will be allowed to progress to R4 level without passing the OMSB Part I Exam. OMSB Registration will be cancelled if a resident does not pass the OMSB Part I in three (3) attempts. OMSB will cover the exam fees for the first attempt only. The examination cost for the second and third attempt will have to be covered by the resident. 3) THE FINAL EXAMINATION FOR THE SPECIALTY CERTIFICATE, PART II EXAM: After a successful completion of the training program the graduate is then eligible to take the OMSB Part II Exam (Exit Exam). The Final Examination may consist of written and oral parts, OSCE, and short clinical cases. The Resident who fails the exam may repeat it within a year after the approval of the Education Committee. The Resident is not allowed to repeat Part II Exam for more than three times. The Residents will be terminated from the Residency training program if he / she does not succeed in the third attempt. However, in exceptional cases, the Resident may be granted a fourth attempt by OMSB. Only those who pass the written part are allowed to sit for the clinical part.
OPTIONAL EXAMINATIONS
OTHER EXAMS:
PROGRESSION CRITERIA:
1. Promotion of a Resident to the next academic level occurs if all rotation
periods during the year have been completed with “Meets Expectations” or higher
global evaluations.  EXIT QUALIFICATIONS:
Criteria for receiving Completion of Training Certificate: |
PROGRAM ACADEMIC ACTIVITIES:
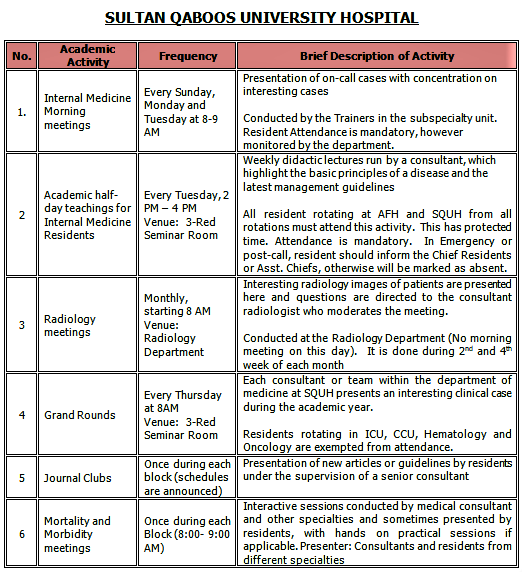
The program conducts various educational activities at each training site for the residents. Attendance to these activities is mandatory and is monitored.
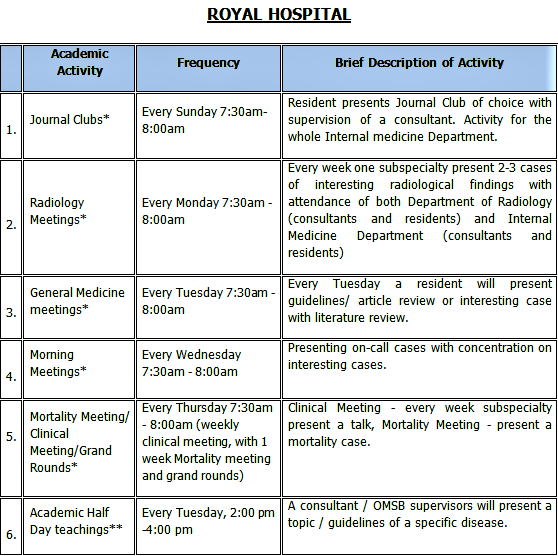 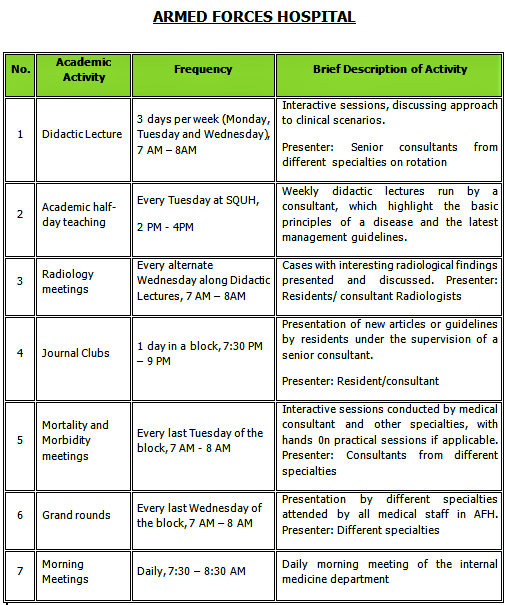 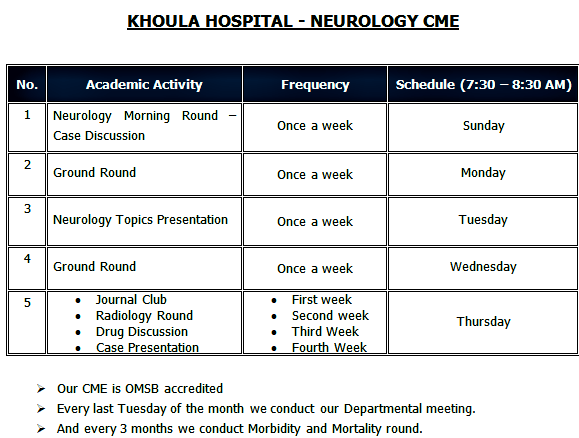 B. SIMULATION SESSIONS
Residents attend the mandatory simulations sessions that are conducted by the
Medical Simulation subcommittee monthly from 1:30 - 4:00 in the OMSB Simulation
Center. SessionsA. Procedural skills. There will be 3 procedures at a time for 2 hours (45 minutes in each room) 1. Thoracentesis 2. Chest tube insertion 3. Lumbar puncture 4. Bone marrow aspiration 5. Central line insertion 6. Arthrocentesis 7. Paracentesis B. Airway management including basic, advanced and difficult for 2 hours (45 minutes each) C. ACLS Refresher Day D. Emergency Management 1. Respiratory Failure 2. Shock 3. Cardiac Emergencies 3. Fundamental Critical Care Support (FCCS) E. R3/R4 residents are under the category of Senior simulation skills group F. Emergency scenarios G. ACLS Refreshers H. Board Communication - MOCK I. Communication skills with actors from College of ART J. Rational Physical Examination Series C. RESIDENT CLUBS The Internal Medicine program conducts Data Interpretation sessions for the residents which are conducted 1 day in a block, 7:30 PM – 9 PM at AFH and Every Sunday 7:30 AM-8:00 AM at Royal Hospital. These activities are conducted and moderated by the subspecialty trainers –attendance in not mandatory- to help the Residents in improving their skills in interpreting the various tests results and patient exams to come up with a diagnosis. Data Interpretation of the following tests:1. Pulmonary Function Test (PFT) 2. Liver Function Test (PFT) 3. Arterial Blood Gas (ABG) 4. Electrocardiogram (ECG) 5. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) 6. Electroencephalogram (EEG) 7. Computer Tomography (CT) 8. Chest X-ray 9. Urea and Electrolytes (U&E) 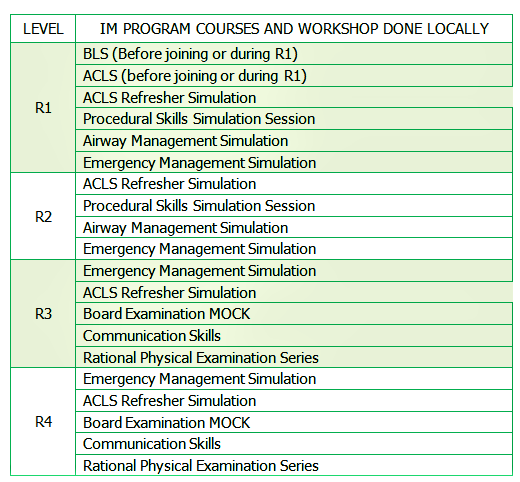 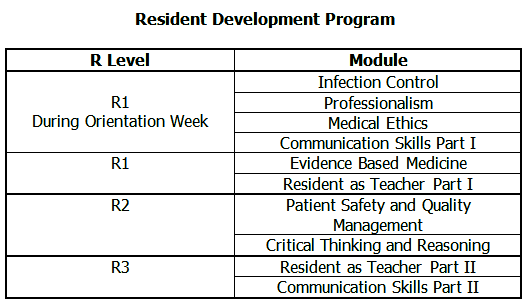 |
Medical Program Executives:
Shari Custodio: 2418-1610
Jhoane Simeon-Lao: 2418-1091
Adrien Villaverde: 2418-1675